Variables are used to compare and manipulate data for display in a report. Variables are not saved to the database--their values are stored in the computer's memory while the report is running. After you exit the report, the variables are erased from memory.
You can use variables to:
- Generate record counts in a report (e.g. how many individuals took courses during a given semester).
- Generate numbered lists (e.g. 1. First person taking course, 2. Second person, etc.).
- Calculate values based on report data (e.g. add the payment amount to the total paid IF the pay type is Cash).
- Create shorthand representations of long expressions (e.g. variable Due represents the function gtdue(rgcrse,rgid) and variable Paid represents gtpaid(rgcrse,rgid)).
- Calculate values then use those values to calculate subsequent values (e.g. Due-Paid).
To create a variable:
- Select Report > Variables to open the Variables window. On this window, you can add new variables, change or delete existing variables or change the order in which the variables are evaluated in a report.
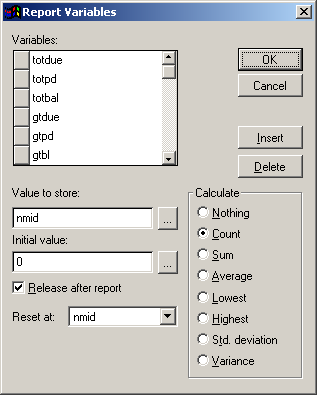
The Variable Definition dialog offers these options:
- Variables: Name of the variable.
- Value to store: Field/Expression which should be stored/calculated in this variable.
- Initial value: Initial value of the variable BEFORE any calculations are performed
- Release after report: Clears the report variable from memory after the report is printed. If not checked, the variable remains in memory until you exit Student Manager.
- Reset at: Specifies the point at which the variable is reset to its initial value. End of Report is the default. Other options include End of Page, End of Column and groups you have created in the report.
- Calculate: Specify a calculation that the variable performs. The variable begins calculating with its initial value, and continues until it is reset.
Notes:
- Report variables are evaluated in the order that they appear in the list and can affect the value of expressions that use them. For example, if variable 1 is used to define the value of variable 2, variable 1 must appear before variable 2.
- If you use a variable in calculations, be sure that you initialize the variable with a non-zero value to avoid a division-by-zero error. If you don't specify a value, Visual FoxPro assigns a default value of 0.
- If you reorder the groups in your report, your report variables might not be resetting on the correct field. For example, if your report has two groups, the first grouping by country and the second grouping by date, and you switch the order of the groups, the variables still reset according to the original positions of the groups.
